Earth Observatory SG on X: Today, the Richter Scale is no longer the preferred method of measuring large earthquakes due to its limitations. More commonly used is the moment magnitude scale as
2. The Rise of Earthquake Science, Living on an Active Earth: Perspectives on Earthquake Science

Moment magnitude, Richter scale - what are the different magnitude scales, and why are there so many?

Full article: Assessing seismicity in Bangladesh: an application of Guttenberg-Richter relationship and spectral analysis

Geosciences, Free Full-Text
SE - The 2022 MW 6.0 Gölyaka–Düzce earthquake: an example of a medium-sized earthquake in a fault zone early in its seismic cycle
What is the Richter scale? Why is it not possible to forecast an earthquake? - Quora

Richter Scale: Most Up-to-Date Encyclopedia, News & Reviews

Earthquake Magnitude Estimation
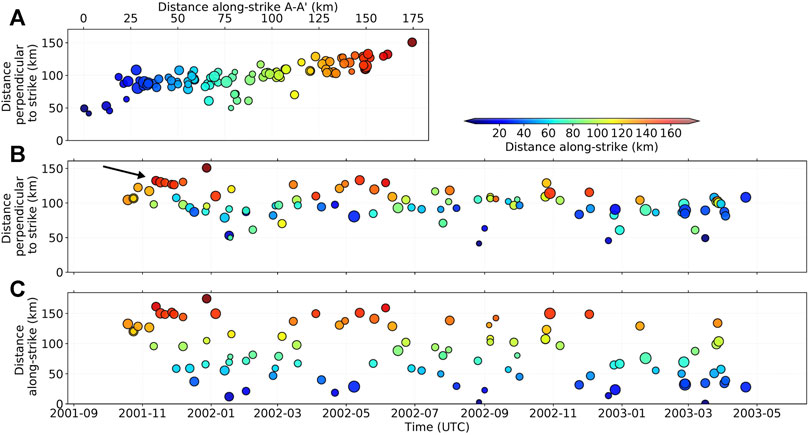
Frontiers Spatio-Temporal Evolution of Intermediate-Depth Seismicity Beneath the Himalayas: Implications for Metamorphism and Tectonics

Earth Observatory SG on X: Today, the Richter Scale is no longer the preferred method of measuring large earthquakes due to its limitations. More commonly used is the moment magnitude scale as

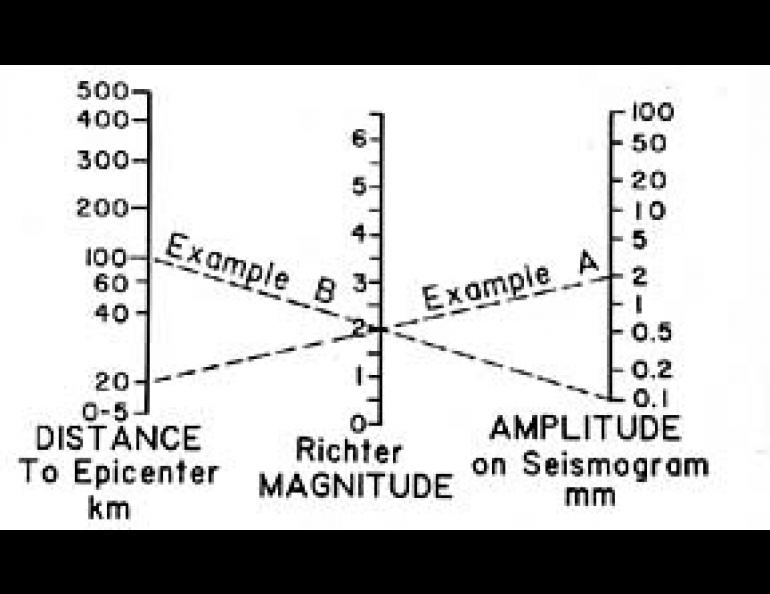
File:How-the-Richter-Magnitude-Scale-is-determined.jpg - Wikipedia

Nucleation of Laboratory Earthquakes: Quantitative Analysis and Scalings - Marty - 2023 - Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth - Wiley Online Library

Earthquake Magnitude

Frontiers Constraining earthquake fault sources through the use of intensity data and seismic scenarios: application to the Betic Cordillera (South Spain)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/seismologist-charles-richter-in-his-lab-515402616-5c7d4cf546e0fb0001edc898.jpg)