Molecular structure of cyanoacrylate and the polymerization process

Molecular structure of cyanoacrylate and the polymerization process

Mechanism of cyanoacrylate polymerization.

Methyl cyanoacrylate molecule, illustration - Stock Image - F029/9620 - Science Photo Library
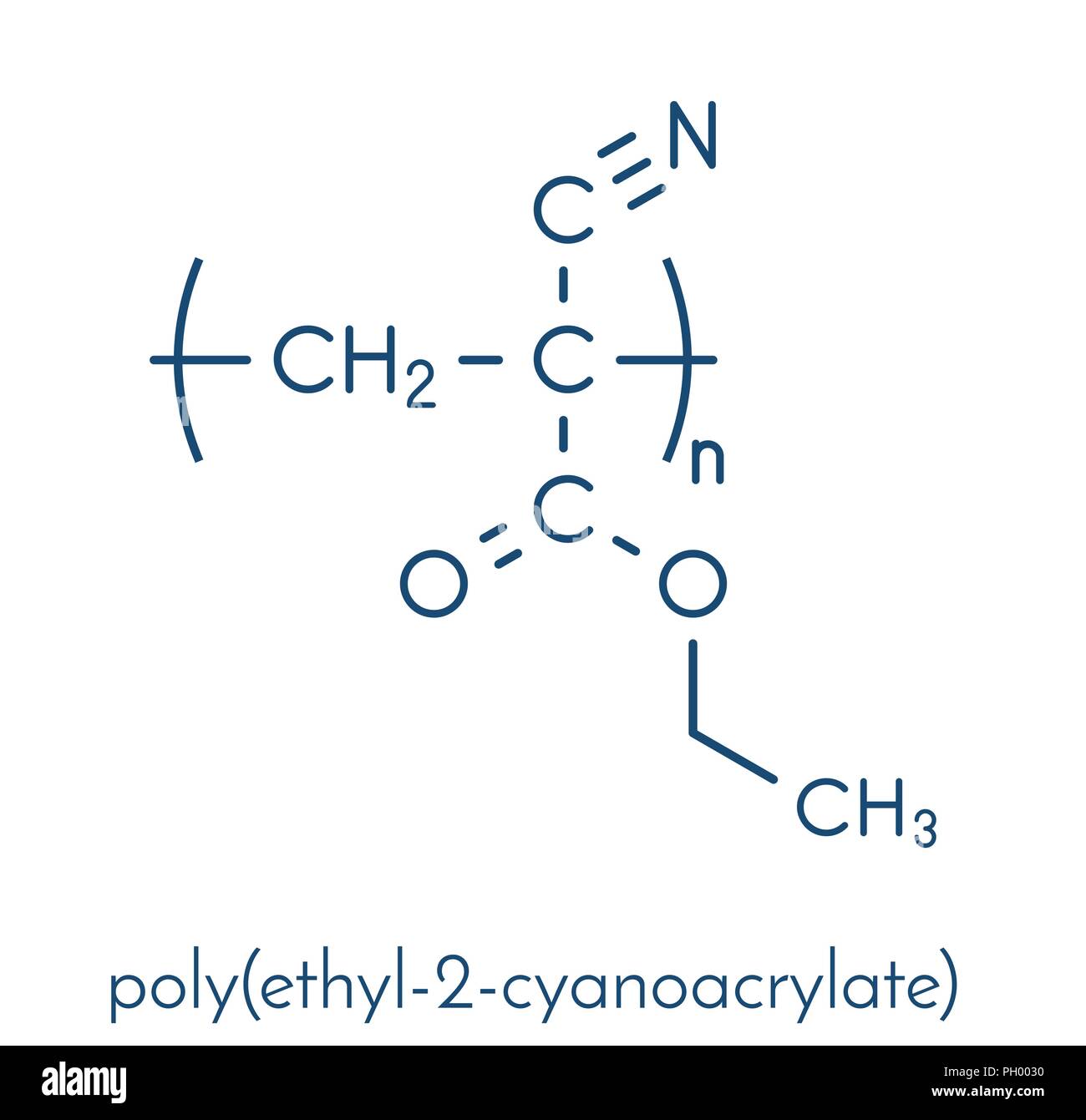
Poly(ethyl cyanoacrylate) polymer, chemical structure. Polymerized (set) form of ethyl cyanoacrylate instant glue. Skeletal formula Stock Vector Image & Art - Alamy

Anionic Polymerization of Ethyl 2-Cyanoacrylate Initiated by 1,3-Dimethylimidazolium (phosphonooxy-)oligosulfanide
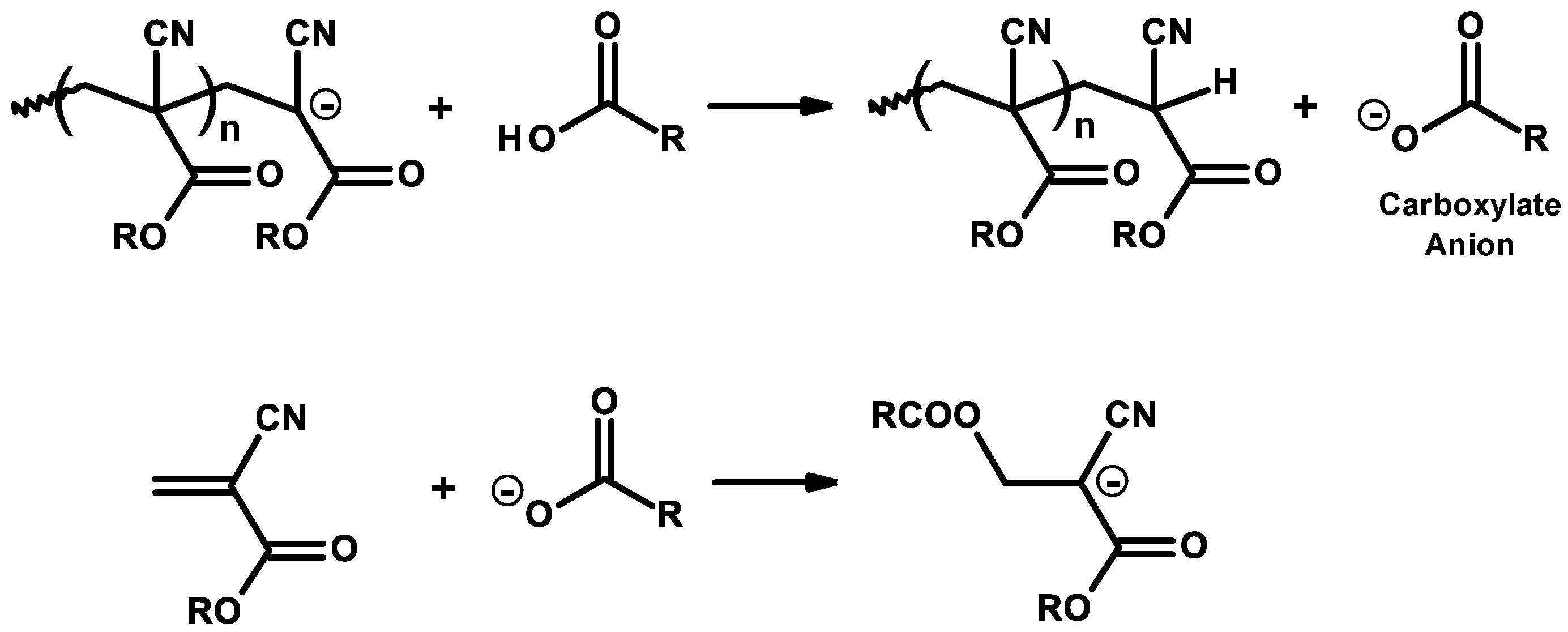
Molecules, Free Full-Text

Major industrial polymers, Types, Examples, & Facts
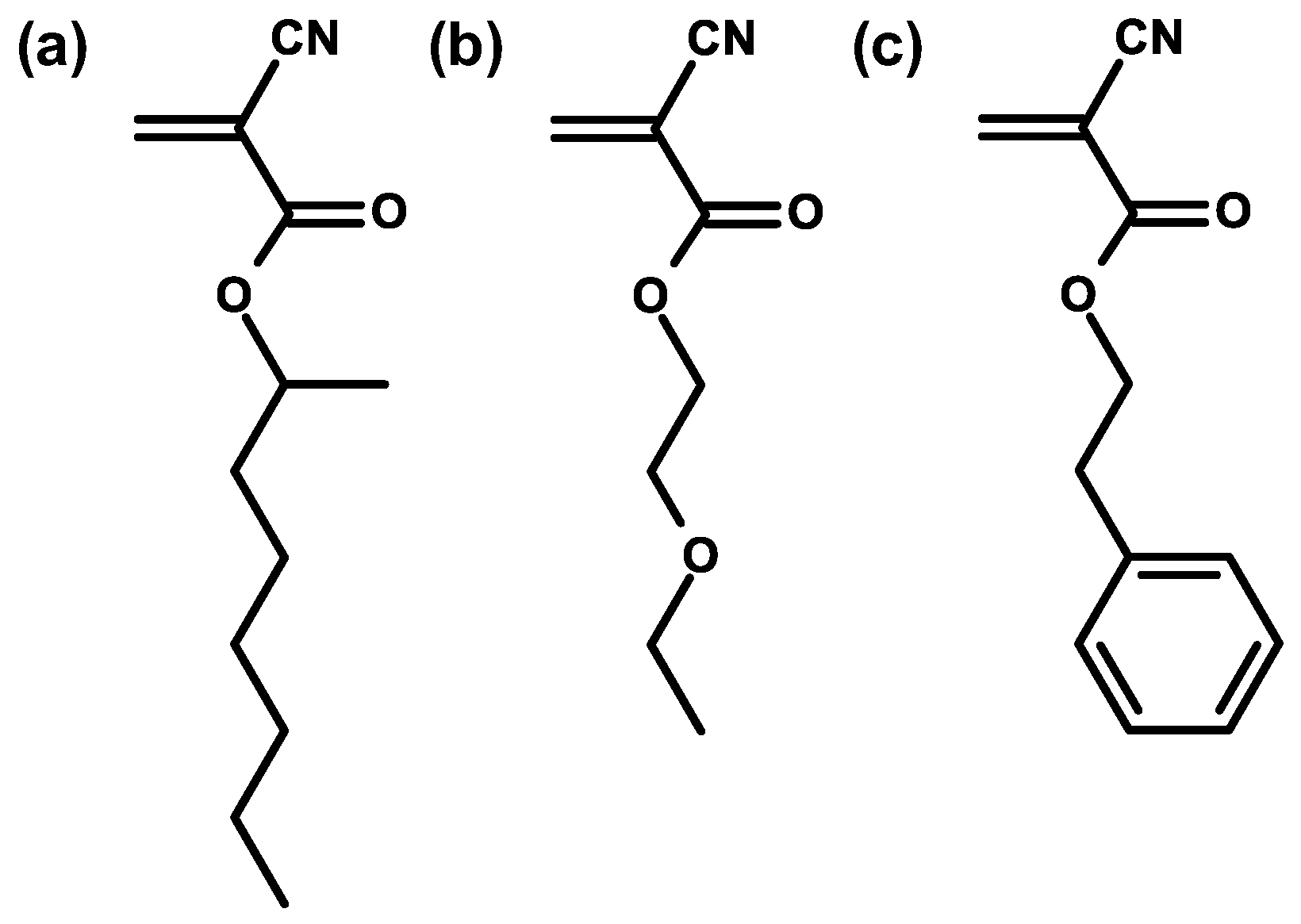
Molecules, Free Full-Text

Bioadhesives SpringerLink

Super glue contains methyl cyanoacrylate, [[Table] which readily polymerizes on exposure to traces of water or alcohols on the surfaces to be bonded together. The polymer provides a strong bond between the
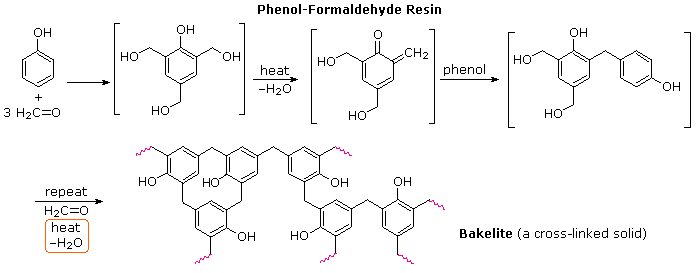
Polymers

Poly(methyl Cyanoacrylate) Polymer, Chemical Structure. Polymerized (set) Form Of Methyl Cyanoacrylate Instant Glue. Skeletal Formula. Royalty Free SVG, Cliparts, Vectors, and Stock Illustration. Image 149278263.
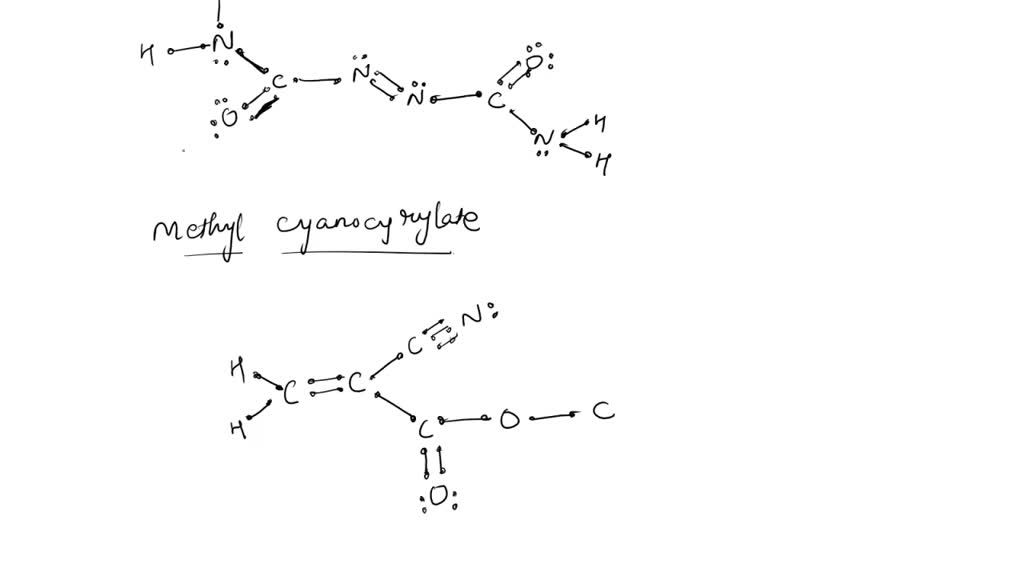
SOLVED: Two molecules used in the polymer industry are azodicarbonamide and methyl cyanoacrylate. Their structures are Azodicarbonamide is used in forming polystyrene. When added to the molten plastic, it decomposes to nitrogen

Cyanoacrylate - an overview









