Gaze-Cueing With Crossed Eyes: Asymmetry Between Nasal and Temporal Shifts
The results highlight the possibility that the gaze-cueing effect might be weakened when a direct gaze exists between the cueing eye and the target and the effect magnitude might depend on which type of face stimulus are used as a cue. A person’s direction of gaze (and visual attention) can be inferred from the direction of the parallel shift of the eyes. However, the direction of gaze is ambiguous when there is a misalignment between the eyes. The use of schematic drawings of faces in a previous study demonstrated that gaze-cueing was equally effective, even when one eye looked straight and the other eye was averted. In the current study, we used more realistic computer-generated face models to re-examine if the diverging direction of the eyes affected gaze-cueing. The condition where one eye was averted nasally while the other looked straight produced a significantly smaller gaze-cueing effect in comparison with when both eyes were averted in parallel or one eye was averted temporally. The difference in the gaze-cueing effect disappeared when the position of one eye was occluded with a rectangular surface or an eye-patch. These results highlight the possibility that the gaze-cueing effect might be weakened when a direct gaze exists between the cueing eye (i.e., nasally oriented eye) and the target and the effect magnitude might depend on which type of face stimulus are used as a cue.

PDF] Gaze and arrow cueing of attention reveals individual differences along the autism spectrum as a function of target context.

Sequence of events in the experiment. Each trial started with a

To follow or not to follow your gaze: The interplay between strategic control and the eye contact effect on gaze-induced attention orienting.

Gaze-Cueing With Crossed Eyes: Asymmetry Between Nasal and Temporal Shifts
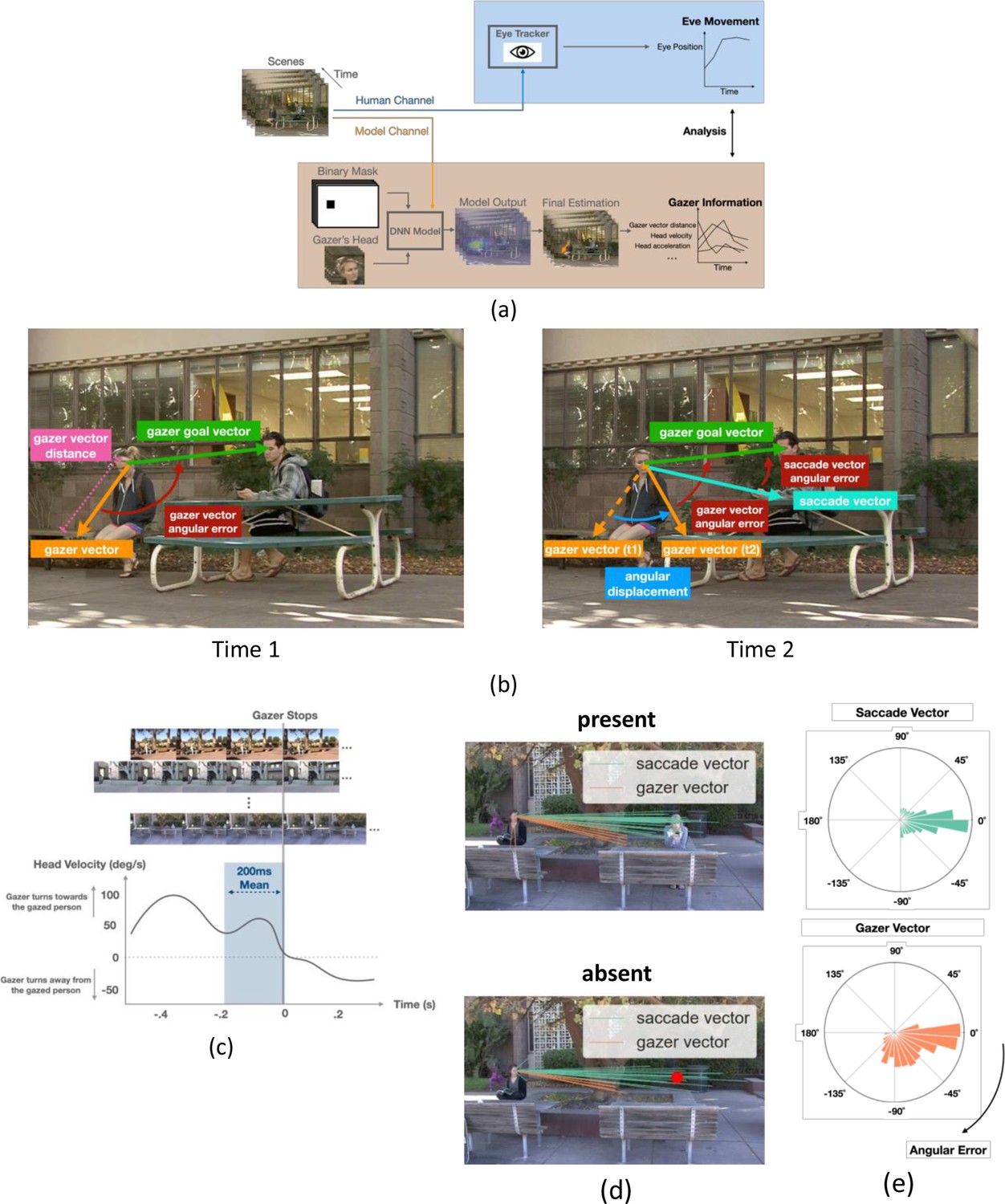
Inferential eye movement control while following dynamic gaze

Gaze-cued shifts of attention and microsaccades are sustained for whole bodies but are transient for body parts

PDF] Searching for asymmetries in the detection of gaze contact versus averted gaze under different head views: a behavioural study.

Full article: Both fearful and happy expressions interact with gaze direction by 200 ms SOA to speed attention orienting

PDF) Cross-cultural asymmetries in oculomotor interference elicited by gaze distractors belonging to Asian and White faces

A Critical Study in Stereopsis and Listing's Law









